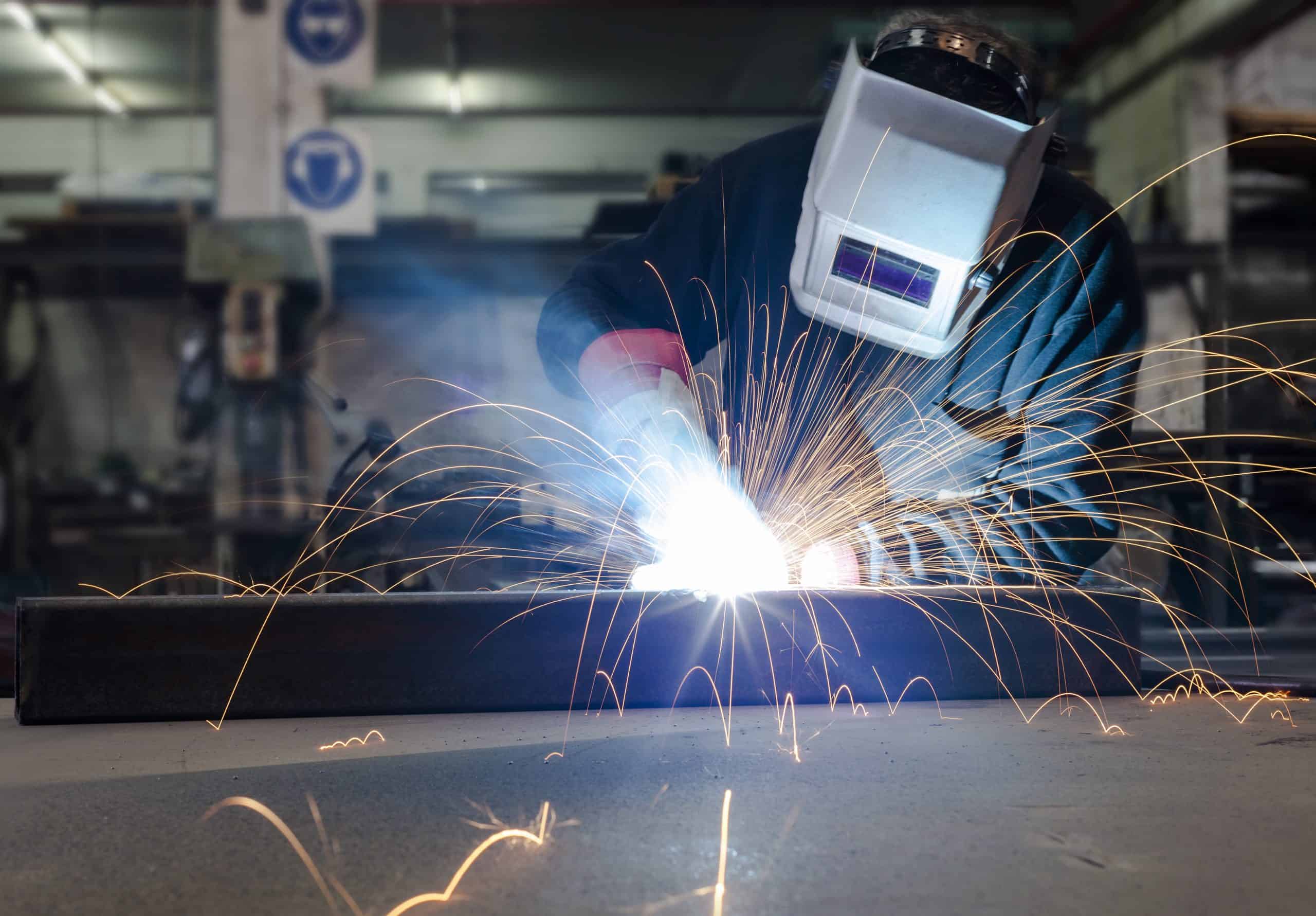
Electric shock
Electric shock is one of the most serious and immediate risks facing a welder. Electric shock can lead to severe injury or death, either from the shock itself or from a fall caused by the reaction to a shock.
Electric shock occurs when welders touch two metal objects that have a voltage between them, thereby inserting themselves into the electrical circuit. For instance, if a worker holds a bare wire in one hand and a second bare wire with another, electric current will pass through that wire and through the welding operator, causing an electric shock. The higher the voltage, the higher the current and, thus the higher the risk for the electric shock to result in injury or death.
The most common type of electric shock is secondary voltage shock from an arc welding circuit, which ranges from 20 to 100 volts. Bear in mind that even a shock of 50 volts or less can be enough to injure or kill an operator, depending on the conditions. Due to its constant change in polarity, alternating current (AC) voltage is more likely to stop the heart than direct current (DC) welders. It is also more likely to make the person holding the wire unable to let go.
To avoid secondary voltage shock, welding operators should
- wear dry gloves in good condition,
- never touch the electrode or metal parts of the electrode holder with skin or wet clothing and
- be sure to insulate themselves from the work and ground,
- keeping dry insulation between their body and the metal being welded or ground (such as a metal floor or wet surface).